Introduction to Technical Analysis
Technical analysis is a methodology used by traders and investors to forecast future price movements based on historical market data. It involves analyzing charts, patterns, and indicators to identify trends and make trading decisions. One crucial aspect of technical analysis is the recognition and interpretation of various patterns that occur within price charts.
Understanding Harmonic Patterns
Harmonic patterns are a subset of technical patterns that use specific geometric price formations to predict future price movements. These patterns are based on Fibonacci ratios and occur naturally in financial markets. Harmonic patterns are popular among traders due to their accuracy in predicting potential reversals or continuation of trends.
Introduction to the Bat Pattern
Among the various harmonic patterns, the Bat pattern is one that stands out for its unique structure and predictive power. It is a type of harmonic pattern that consists of specific Fibonacci retracement and extension levels. The Bat pattern is categorized as a reversal pattern, indicating a potential change in the direction of the price trend.
History and Development of the Bearish Bat Pattern
The concept of harmonic patterns, including the Bat pattern, originated from the work of H.M. Gartley in the early 20th century. Over time, traders and analysts have further developed and refined these patterns, incorporating additional tools and techniques to enhance their effectiveness in trading strategies.
Structure of the Bearish Bat Pattern
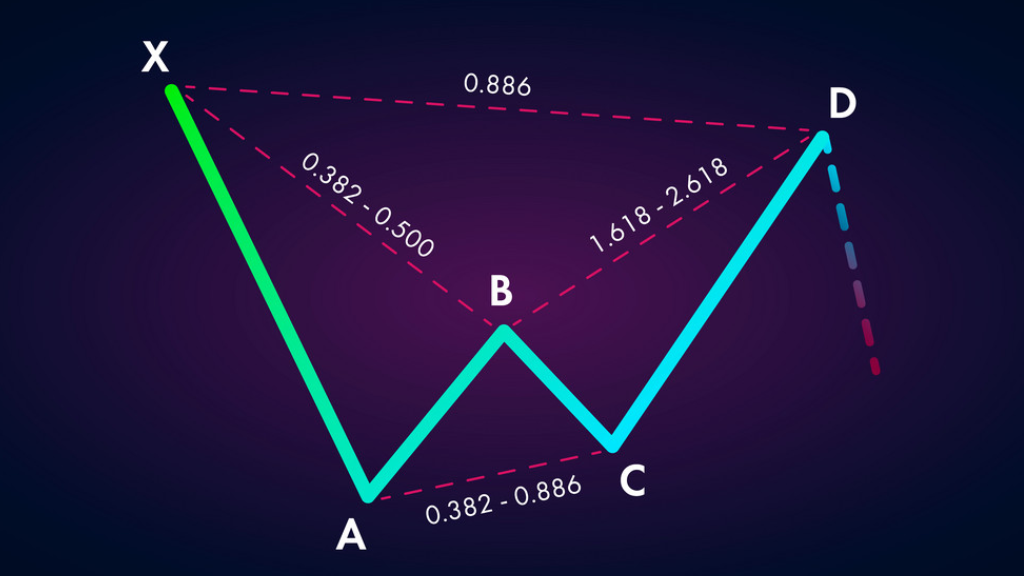
The Bearish Bat pattern consists of four main legs: XA, AB, BC, and CD. The XA leg represents the initial price move, followed by a retracement in the AB leg. The BC leg involves an extension beyond the XA leg, followed by a retracement in the CD leg. The completion of the CD leg marks the potential reversal point of the pattern.
Fibonacci Relationships within the Bearish Bat Pattern
Fibonacci ratios play a crucial role in defining the structure of the Bearish Bat pattern. These ratios, such as 0.382, 0.500, and 0.886, are derived from the Fibonacci sequence and are used to identify potential reversal points within each leg of the pattern. Traders often use Fibonacci retracement and extension tools to measure these ratios accurately.
Recognizing and Identifying Bearish Bat Patterns
Identifying Bearish Bat patterns requires a keen eye for specific price structures and Fibonacci relationships within price charts. Traders look for key characteristics, such as specific retracement and extension levels, to confirm the presence of a Bearish Bat pattern. Additionally, pattern recognition tools and indicators can aid in identifying and confirming these patterns.
Psychology Behind the Bearish Bat Pattern
The Bearish Bat pattern reflects underlying market psychology and sentiment during each leg of the pattern formation. For instance, the AB leg represents a temporary retracement in the direction of the prevailing trend, while the BC leg signifies a continuation of the trend with increased momentum. Understanding market psychology can help traders anticipate potential price movements.
Trading Strategies Using the Bearish Bat Pattern
Traders employ various trading strategies when trading Bearish Bat patterns. Entry points are typically identified near the completion of the CD leg, with stop-loss orders placed above the pattern’s high. Risk management techniques, such as position sizing and trailing stops, are essential to mitigate potential losses and maximize profits.
Confirmation and Validation Techniques
To enhance the reliability of Bearish Bat patterns, traders often use additional confirmation techniques. These may include the use of other technical indicators, such as oscillators or moving averages, to validate the pattern’s signals. Backtesting strategies and historical analysis can also provide valuable insights into the pattern’s effectiveness in different market conditions.
Case Studies and Examples
Examining real-life examples of Bearish Bat patterns can provide valuable insights into their application and effectiveness in trading. Analyzing past trades and outcomes can help traders understand the nuances of pattern recognition and refine their trading strategies accordingly.
Common Mistakes and Pitfalls
Despite their predictive power, Bearish Bat patterns are not infallible, and traders may encounter common mistakes and pitfalls when trading them. These may include overreliance on patterns alone, ignoring fundamental analysis, and failing to adapt to changing market conditions.
Advantages of Trading with the Bearish Bat Pattern
Trading Bearish Bat patterns offers several advantages, including high probability trading setups and the potential for favorable risk-reward ratios. By identifying these patterns accurately and executing well-planned trading strategies, traders can capitalize on price reversals and maximize their trading profits.
Limitations and Challenges
While Bearish Bat patterns can be powerful trading tools, they are not without limitations and challenges. Traders may encounter false signals and failed patterns, requiring them to exercise caution and discretion when trading. Additionally, adapting to changing market conditions and remaining disciplined can be challenging for traders.
Combining the Bearish Bat Pattern with Other Strategies
To enhance trading outcomes, traders often combine the Bearish Bat pattern with other technical analysis tools and strategies. This may include looking for confluence with support and resistance levels, trendlines, or other harmonic patterns to increase the probability of successful trades.
Risk Management and Capital Preservation
Effective risk management is essential when trading Bearish Bat patterns to preserve capital and minimize losses. Traders should employ proper position sizing techniques, set stop-loss orders, and adhere to strict risk-reward ratios to protect their trading capital over the long term.
Backtesting and Optimization
Backtesting trading strategies based on Bearish Bat patterns is crucial to evaluate their effectiveness and refine them over time. By analyzing historical data and conducting thorough testing, traders can identify the optimal parameters and settings for their trading strategies.
Psychological Considerations
Successful trading requires more than just technical analysis skills; it also involves managing emotions and maintaining discipline. Traders must learn to control fear, greed, and other emotions that can cloud judgment and lead to impulsive decisions. Developing a disciplined mindset and sticking to a well-defined trading plan are essential for long-term success.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Bearish Bat pattern is a powerful tool in the arsenal of technical traders, offering valuable insights into potential market reversals. By understanding its structure, recognizing key characteristics, and employing effective trading strategies, traders can harness the predictive power of Bearish Bat patterns to enhance their trading outcomes.
FAQs
What is a Bearish Bat pattern in trading?
A Bearish Bat pattern is a specific harmonic pattern formed by four distinct price swings, indicating a potential reversal in the direction of the prevailing trend.
How do I recognize a Bearish Bat pattern on a price chart?
Look for specific Fibonacci ratios between price swings, including the XA, AB, BC, and CD legs. The completion of the CD leg near Fibonacci retracement and extension levels confirms the pattern.
What trading strategies can I use with Bearish Bat patterns?
Traders often wait for the completion of the CD leg to enter short positions, placing stop-loss orders above the pattern’s high. Risk management techniques and additional confirmation tools can enhance trading outcomes.
Are Bearish Bat patterns always reliable for trading decisions?
While Bearish Bat patterns have high predictive power, they are not foolproof. Traders should exercise caution and combine pattern recognition with other technical analysis tools for confirmation.
How can I improve my trading skills with Bearish Bat patterns?
Practice identifying Bearish Bat patterns on historical price charts and backtest trading strategies using demo accounts. Additionally, continuous learning and staying updated on market developments are essential for refining trading skills.