In the digital age, the Internet of Things (IoT) has emerged as a transformative force, reshaping industries and revolutionizing the way we interact with technology. IoT refers to the network of interconnected devices, sensors, and software applications that enable the exchange of data and communication over the Internet. As we delve into the realm of IoT integration in Genesis, it is essential to understand its significance and impact on technological innovation.
Genesis, in the context of technology, represents the foundation or origin of creation and innovation. It encompasses various sectors, including smart homes, industrial automation, healthcare, agriculture, transportation, energy, and the environment. By integrating IoT into Genesis, we can unlock new possibilities, optimize processes, and drive efficiencies across diverse domains.
Understanding Genesis
Genesis, in the technological landscape, signifies the beginning or inception of innovation. It traces back to the evolution of technology, from its rudimentary forms to the sophisticated systems and solutions we have today. Genesis serves as the cornerstone of progress, driving advancements in various sectors and laying the groundwork for future developments.
Exploring IoT
IoT is a game-changer in the digital era, facilitating seamless connectivity and data exchange between devices and systems. It comprises interconnected networks of sensors, actuators, and software applications that collect and transmit data over the internet. The evolution of IoT technology has led to the proliferation of smart devices and solutions, revolutionizing how we interact with our surroundings.
Integration of IoT in Genesis
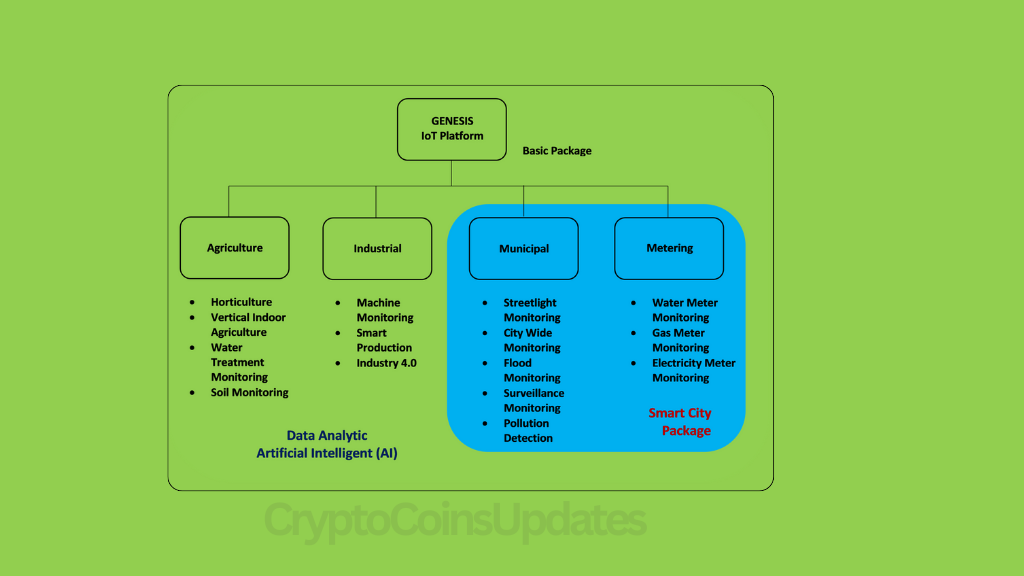
The integration of IoT in Genesis holds immense potential across multiple sectors. In smart homes and buildings, IoT-enabled devices enhance comfort, security, and energy efficiency. Industrial automation leverages IoT for real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and process optimization. In agriculture, IoT solutions enable precision farming techniques, improving crop yields and resource utilization.
Benefits of IoT Integration
The integration of IoT in Genesis offers a myriad of benefits. It enhances efficiency and productivity by streamlining processes and automating routine tasks. IoT enables data collection and analysis, providing valuable insights for informed decision-making. Moreover, IoT integration leads to cost savings, resource optimization, and improved user experiences across different sectors.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its transformative potential, IoT integration in Genesis presents several challenges and limitations. Security and privacy concerns loom large, as interconnected devices are susceptible to cyber threats and data breaches. Interoperability issues, data management challenges, and scalability constraints also pose significant hurdles to seamless IoT deployment and adoption.
Case Studies
Real-world examples demonstrate the tangible impact of IoT integration in Genesis. Smart cities leverage IoT technologies to enhance urban infrastructure, improve public services, and optimize resource management. Precision agriculture employs IoT-enabled sensors and drones to monitor soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health, thereby boosting agricultural productivity and sustainability.
Future Trends and Innovations
The future of IoT in Genesis promises continued innovation and evolution. Advancements in edge computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and blockchain technology are poised to revolutionize IoT applications across various sectors. Edge computing brings processing power closer to IoT devices, enabling real-time data analysis and decision-making. AI integration enhances the capabilities of IoT systems, enabling predictive analytics and personalized experiences. Blockchain technology ensures data integrity, security, and transparency in IoT transactions and interactions.
Ethical and Societal Implications
As IoT integration in Genesis expands, it raises ethical and societal concerns that warrant careful consideration. Privacy rights, data security, and ownership issues are paramount, requiring robust regulations and frameworks to safeguard user interests. Moreover, the societal implications of widespread IoT adoption, such as job displacement and digital divide, necessitate proactive measures to address potential challenges and ensure equitable access to IoT technologies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, IoT integration in Genesis represents a paradigm shift in technology, offering transformative opportunities for innovation and growth. By harnessing the power of IoT responsibly, we can drive sustainable development, enhance quality of life, and create a more connected and efficient world. As we navigate the complexities and possibilities of IoT in Genesis, it is imperative to prioritize ethical considerations, address challenges, and embrace emerging trends to unlock its full potential for the benefit of society.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions) with Answers:
What is meant by “genesis innovation,” and how does IoT contribute to it?
Genesis innovation refers to the early stages of developing innovative ideas and technologies, and IoT plays a crucial role by providing interconnectedness and data insights that drive creativity and problem-solving.
Can you provide examples of industries benefiting from IoT-driven genesis innovation?
Industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, agriculture, transportation, and smart cities are leveraging IoT to drive innovation in areas like remote patient monitoring, predictive maintenance, precision farming, logistics optimization, and urban infrastructure management.
What challenges do organizations face when implementing IoT solutions for genesis innovation?
Challenges may include security concerns, interoperability issues, data privacy risks, scalability limitations, and the need for skilled talent. Overcoming these challenges requires robust strategies, collaboration, and investment in technology infrastructure.
How does IoT foster collaboration and synergy in the genesis phase of innovation?
IoT enables seamless communication and data exchange between devices, systems, and stakeholders, facilitating collaboration across teams, departments, and organizations. This collaboration leads to the synthesis of ideas and the development of innovative solutions.
What are the key components of an IoT ecosystem that drive genesis innovation?
Key components include sensors, actuators, connectivity technologies (such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular networks), edge computing, cloud platforms, data analytics, and artificial intelligence/machine learning algorithms.
How can startups leverage IoT to drive genesis innovation on a limited budget?
Startups can utilize low-cost IoT development kits, open-source software frameworks, cloud-based platforms with pay-as-you-go models, and collaborative ecosystems (such as innovation hubs and accelerators) to access resources and expertise.
What role does data play in IoT-driven genesis innovation, and how is it managed effectively?
Data generated by IoT devices is valuable for informing decision-making, identifying trends, and optimizing processes. Effective data management involves collection, storage, processing, analysis, and visualization using robust tools and techniques.
How does IoT contribute to sustainability and environmental conservation in genesis innovation?
IoT enables the monitoring and optimization of resource usage, energy consumption, waste management, and environmental conditions, leading to more sustainable practices and reduced ecological footprint in innovation processes.
What are some emerging trends in IoT that will shape the future of genesis innovation?
Emerging trends include edge computing, 5G connectivity, digital twins, blockchain integration, augmented reality/virtual reality, and autonomous systems, which will enhance IoT capabilities and drive innovation across various domains.
How can companies ensure the security and privacy of IoT devices and data in genesis innovation projects?
Companies can implement robust cybersecurity measures such as encryption, access controls, authentication mechanisms, regular security audits, and compliance with industry standards to protect IoT devices and data from cyber threats and breaches.